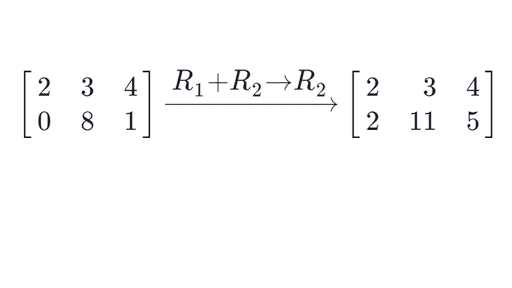Can We Use Both Row And Column Transformation In Matrices
D C3r1r3r3 2 4 1 1 2 0 0 2 8 7 0 1 4 5 3 5. Row and column vectors are operated upon by matrices rows on the left and columns on the right.

Can I Exchange Column And Then Use The Row Transformation When Converting A Matrix Into A Row Echelon Form Mathematics Stack Exchange
Another n n matrix Q can act on p Then one can write t p Q v MQ so the matrix product transformation MQ.
Can we use both row and column transformation in matrices. If you multiply the first column of the matrix by 3 both equations change into something thats not equivalent to what they were before. For to be the inverse of you need or equivalently and you have. Last updated at April 4 2019 by Teachoo.
Det A det P det Q det A. Again we need to transform this submatrix to that with the flrst nonzero column 1 0. Interchange two rows or columns.
Example - R 1 R 3 C 2 C 1. An n n matrix M can represent a linear map and act on row and column vectors as the linear maps transformation matrix. So if we multiply the i th row of a matrix by a non-zero number k symbolically it can be denoted by R.
The entire first equation is multiplied by 3. For most purposes you cant do both row and column transformations. Matrix multiplication is not commutative so there is no reason for the latter identity imply the former.
For a row vector v the product vM is another row vector p. Since text reads from left to right column vectors are preferred when transformation matrices are composed. If A and B are the matrices of two linear transformations.
As the name suggests only the rows of the matrices are transformed and NO changes are made in the columns. Row operations preserve the solution set of the system of equations. If you multiply the first row of the matrix by 3 you get an equivalent system of equations.
To multiply a matrix A to a matrix B you should multiple each row of the first matrix to each column of the second matrix. A P A Q. The elements of any row or column of a matrix can be multiplied with a non-zero number.
Like row case one can produce a unique RCEF for any matrix. There is fairly little practical use for doing so however. Similarly it is asked can we use both row and column transformation in determinant.
If youre solving a system of linear equations you can only do row operations. Example - R 1 2R 1 C 3 -85 C 3. You dont have to do just a sequence of row ops or just a sequence of column ops.
Now we can forget about the flrst row and concentrate on submatrix of D consist-ing of the other rows. Now add 3 times row 1 of C to its third row to get a matrix with the flrst column of desired form. The elementary matrix operations are.
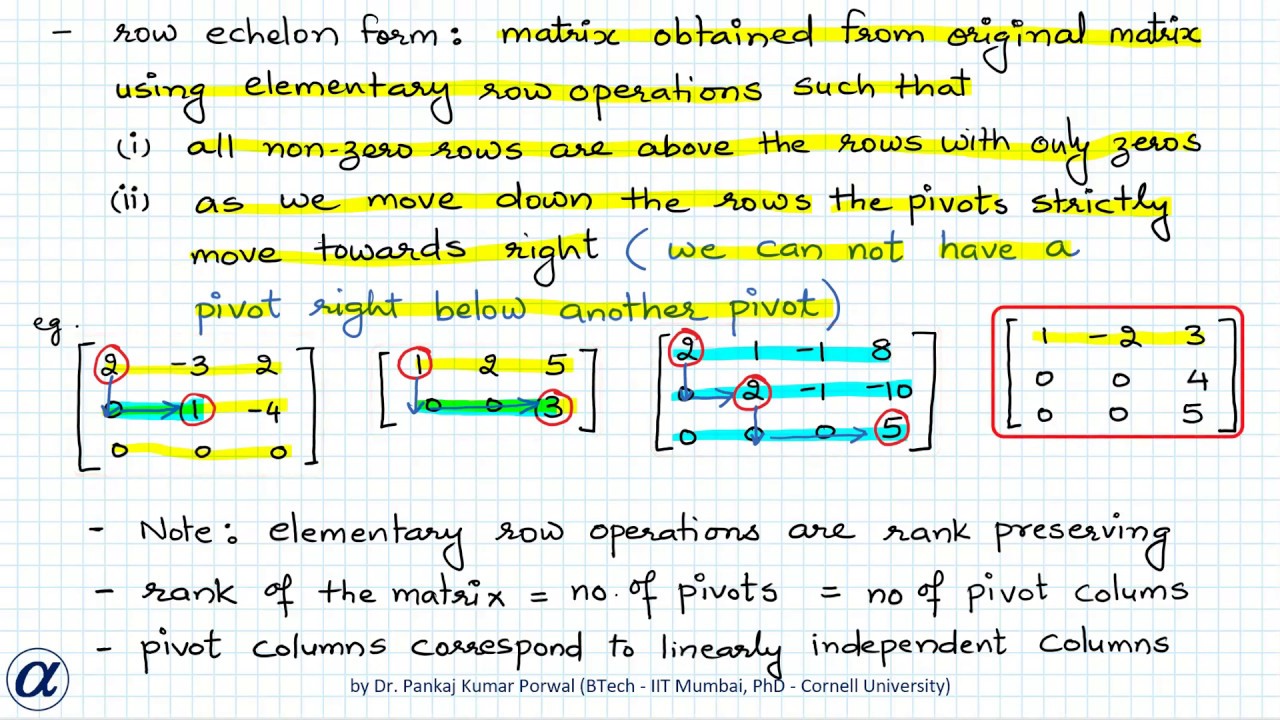
Column operations correspond to changing the variables If all you want to know is the rank of a matrix but you dont care about anything else then you can do both row and column. In examples of matrices in CEF above flrst and third matrices are in RCEF and the second is not. Check this I only tried this on a 2 2 example These problems aside yes you can use both column operations and row operations in a Gaussian elimination procedure.
If you add column 1 to column 2 x 1 x 1 x 2. You can do a sequence of row and column ops each of which adds a factor to the determinant until you reach the identity. Multiply a row or column by a non-zero number.
Row addition factor 1 row transposition factor 1 and row multiplication by c factor c n where n n is the size of the matrices. Here det P and det Q are factors that depends on your exact operations. Once the matrix is converted into its echelon form count the number of non zero rows or non zero columns.
Just use one or the other. After both row a column operations you have. Add a row or column to another multiplied by a non-zero.
To this end we procede in a similar way. If you perform both row and column operations you get two matrices and such that so in the right hand side you get. Applying column transformations is not allowed in solving linear systems1.
Where i is the index of the row in A and j is the index of a column in B. These row operations are executed according to a certain set of rules which make sure that the transformed matrix is equivalent to the original matrix. Each such product is the element of the resulting matrix at i j position.
By applying row transformation or column transformation the given matrix is transformed into its echelon form. Row and column operations can make a matrix nice matrix has a row-reduced form and a column-reduced form but lets study rows whichwe obtain by row operations to make it as simple as possible. We use elementary operations to find inverse of a matrix.
If the original equation had been written as. Any row containing the leading one of a column consists of all zeros except this leading one. The number of non zero rows or the non zero columns is called the rank of the matrix.
This form is such that.

A Complete Beginners Guide To Matrix Multiplication For Data Science With Python Numpy By Chris The Data Guy Towards Data Science

Chapter 1 Matrices Determinants Session Objectives Meaning Of

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math
Can You Use Both Mix Row And Column Operations In Finding The Rank Of A Matrix Quora

Introduction To Matrices Boundless Algebra

Difference Between A Row Column Vector Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math

Elementary Operations On A Matrix Rows And Columns Teachoo
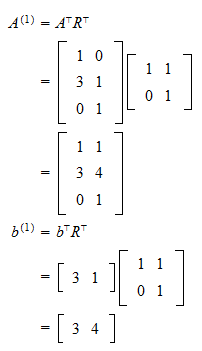
Elementary Column Operations Matrix Algebra

Matrix Representation Wikipedia

Elementary Operations On A Matrix Rows And Columns Teachoo
Rank Of A Matrix And Methods To Find The Rank Minor Method And Row Echelon Form Method Youtube
Http Www Math Ucla Edu Tao Resource General 115a 3 02f Week6 Pdf
Can You Use Both Mix Row And Column Operations In Finding The Rank Of A Matrix Quora

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math
Matrix Row Operations Article Matrices Khan Academy

Elementary Operations On A Matrix Rows And Columns Teachoo