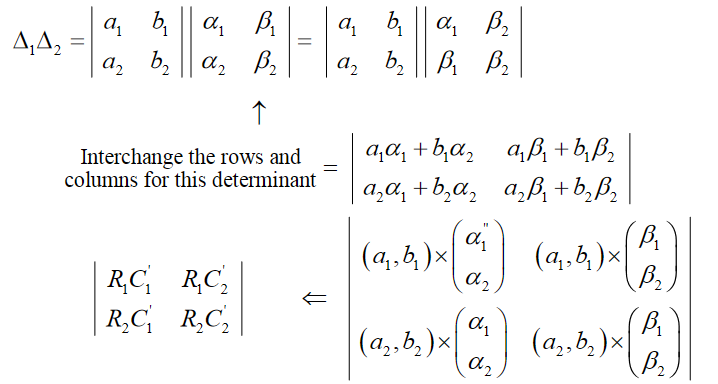Determinant Of Matrix Multiplied By Constant
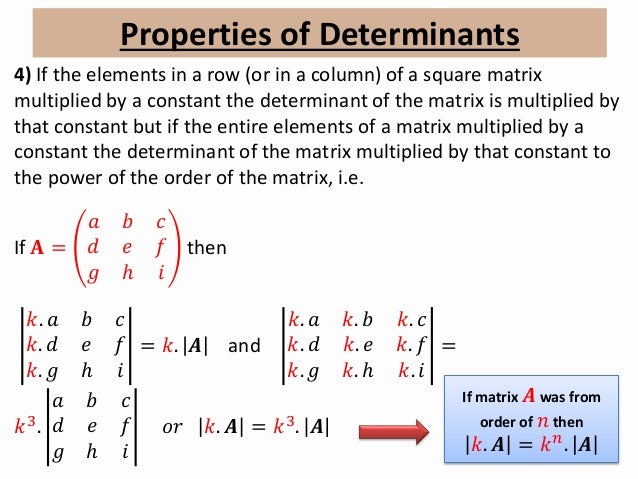
If we multiply a scalar to a matrix A then the value of the determinant will change by a factor. Multiplying a column of a matrix by a nonzero constant results in the determinant being multiplied by the same nonzero constant.
Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 6 Of 48 Example Of Rule 1 Multiplying By A Constant Youtube
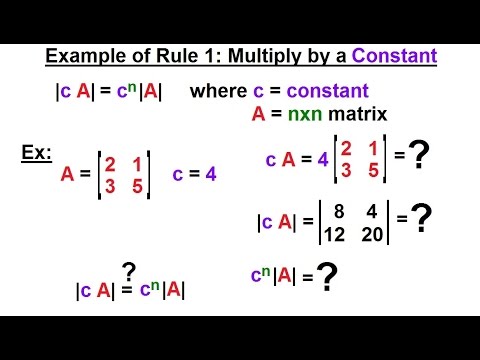
Scalar Multiple Property If any row or column of a determinant is multiplied by any scalar value that is a non-zero constant the entire determinant gets multiplied by the same scalar that is if any row or column is multiplied by constant k the determinant value gets multiplied by k.

Determinant of matrix multiplied by constant. Property 6 states that if any row or column of a matrix is multiplied by a constant the determinant is multiplied by the same factor. Directly from the definition of the determinant. If matrix X-1 is the inverse of matrix X then det X-1 1det x detX-1 If two square matrices x and y are of equal size then det XY det X det Y If matrix X retains size a a and C is a constant then det CX C a det X.
Det A Sum of -1 ij aij det A ij n2. A11a22 - a12a21 n2. C g i ac g i and its going to be minus F times you get rid of that row that de gh the determinant of de gh thats the determinant of this matrix a now what if we define some new matrix here lets call it a prime let me may scroll down a little bit let me define a prime right here a.
Ive tried to write it out as int he question but where ive wrote sum of this is sigma. Created by Sal Khan. Determinant when row is added.
Det B k a k d k b k c k 2 a d k 2 b c k 2 a d b c k 2 det A. Furthermore we note that EA results from multiplying a row in A by k so we have detEA k det A. Correction scalar multiplication of row.
We thus know that the determinant of this matrix is detE k. In the most simplest of case say a matrix A which is a 2 2 matrix multiplying it by a constant k gives the following general setup. 2 a1b1c1 α2β2γ2 a1α2 b1β2c1γ2 R 1 R 2 a 1 b 1 c 1 α 2 β 2 γ 2 a 1 α 2 b 1 β 2 c 1 γ 2 As in the 2 2 case we can have row-by-column and column-by-column multiplication.
K a b c d k a k b k c k d The determinant is therefore writing B k A. This makes sense since we are free to choose by which row or column we will expand the determinant. The determinant when a row is multiplied by a scalar.
Making the substitution that detE k we get that detEA detE detA. Created by Sal Khan. The determinant when a row is multiplied by a scalar.
Rhombus5 If we multiply each element of a row or a column of a determinant by constant k then value of determinant is multiplied by k. To gain a little practice let us evaluate the numerical product of two 3 3 determinants. If we multiply one row with a constant the determinant of the new matrix is the determinant of the old one multiplied by the constant that is In particular if all the entries in one row are zero then the determinant is zero.
If an entire row or an entire column of Acontains only zeros then. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. The determinant when one matrix has a row that is the sum of the rows of other matrices and every other term is identical in the 3 matrices.
True If two rows of a square matrix are equal then its determinant is 0. If each element of a row or column of a determinant is multiplied by a constant k then the value of the determinant gets multiplied by k. If we choose the one containing only zeros the result of course will be zero.
Or multiplying a determinant by any constant k say means multiply each element of only one row or column by k. Constants may be any real number. If each element of a row or column is multiplied by a constant then the value of the determinant gets multiplied by the constant.
Rhombus5 Multiplying a determinant by k means multiply elements of only one row or one column by k. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Rhombus5 If 3 3 3 A thenA A ij a k k rhombus5 If elements of a row or a column in a determinant.
Show for n 2 first then show that the statement is true if one assumes it is true for n-1 n-1 matrices.

Operations On Determinants Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 31 Of 48 Multiplying By A Constant 2x2 Determinants Youtube

Multiplicative Inverses Of Matrices And Matrix Equations Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Determinant When Multiplying A Matrix By A Constant Youtube

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 31 Of 48 Multiplying By A Constant 2x2 Determinants Youtube

Inverting Matrices Determinants And Matrix Multiplication Ppt Download

Determinant When Row Multiplied By Scalar Video Khan Academy
Multiplication Of Determinants What Is Multiplication Of Determinants Examples Solutions Cuemath

Matrices Matrix Multiplication Warm Up Subtract Don T Forget To Kcc Ppt Download

The Determinant Of A 3 X 3 Matrix General Shortcut Method Studypug
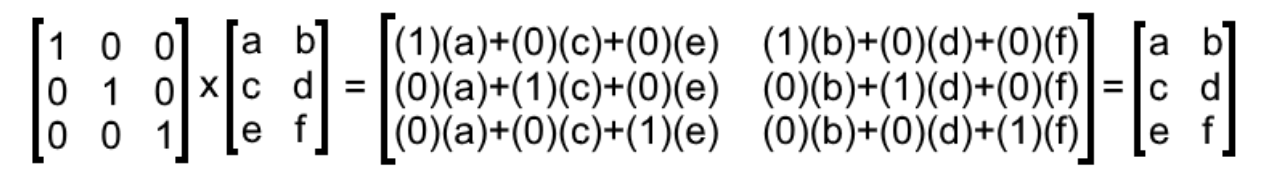
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug

Properties Of Determinants Of Matrices Geeksforgeeks
Properties Of Matrix Scalar Multiplication Article Khan Academy
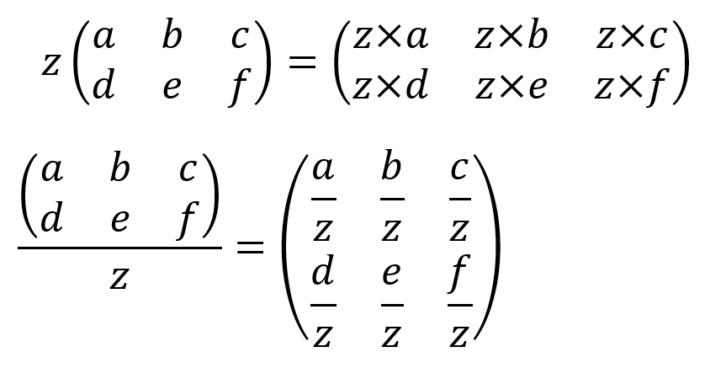
Introduction To Matrix Calculations The Information Lab

Determinant Multiplied By Constant Youtube