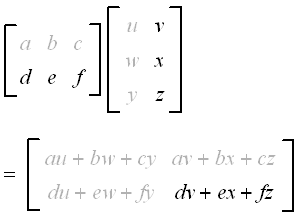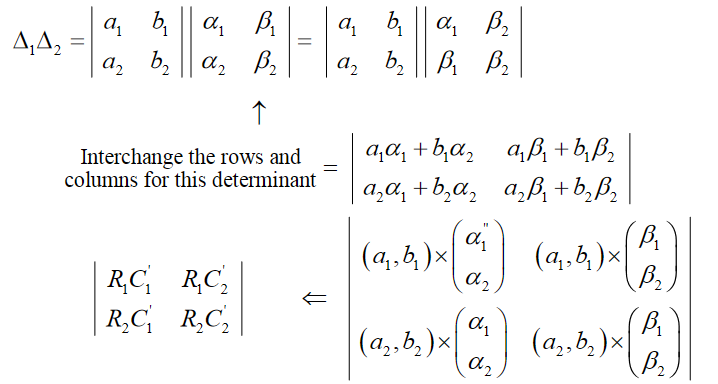Matrix Product Rule Determinant
So a strategy to compute the determinant of a matrix is to transformthe matrix into a row-echelon matrix using elementary row transformationsrecording how these elementary row. In this case it is clear that MA i1 and M B i1 are the same except for two rows being swapped.

How Does Computing The Determinant Of A Matrix With Unit Vectors Give You The Cross Product Mathematics Stack Exchange
Free matrix determinant calculator - calculate matrix determinant step-by-step.

Matrix product rule determinant. A matrix is often used to represent the coefficients in a system of linear equations and the determinant can be used to solve those equations. Therefore Ai1 Bi1. Recall fromthe previous section that the determinant of a triangular matrix is the productof the entries on its diagonal.
This theorem is very important for computing determinants. Well prove this in two cases rst whenis an elementary matrix. One of definitions of the determinant isdet mathbf C sum_lambda in S_n operatorname sgn lambda prod_k1n C_k lambda kI want to prove from this that.
The matrix must be square equal number of columns and rows to have a determinant. B 1A 1AB B 1A 1AB B 1IB B 1IB B 1B I and ABB 1A 1 ABB 1A 1 AIA 1 AIA 1 AA 1 I. BecausedetE 1for a combination rule detE 1for a swap rule anddetE cfor a multiply rule with multiplierc6 0 it follows that for any elementarymatrixEthere is thedeterminant multiplication rule detEA detE detA.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. If two rows of a matrix are equal its determinant is zero. The determinant of a matrix is a scalar value that is used in many matrix operations.
The determinant of the upper triangular matrix equal to the product of its diagonal elements. A a b c d. The n n matrices that have an inverse form a group under matrix multiplication the subgroups of which are called matrix groups.
Ie AT ij A ji ij. The determinant of a matrix product is the product of the determinants. College algebra introduces matrix notation and determinant notation.
A matrix in row-echelon form is a triangularmatrix. By using this website you agree to our Cookie Policy. The determinant of the product oftwo square matrices is the product of their deter-minants that isjABj jAj jBj.
Matrix transpose AT 15 33 52 21 A 1352 532 1 Example Transpose operation can be viewed as flipping entries about the diagonal. The determinant of a product of square matrices is the product of the determinants of the factors. Evaluation of a 2 2 determinant is by Sarrus Rule.
For a 22 matrix the determinant is ad - bc For a 33 matrix multiply a by the determinant of the 22 matrix that is not in a s row or column likewise for b and c but remember that b has a negative sign. Using the associative law for matrix multiplication repeatedly gives. Easily proved using the formula for the determinant of a 2 2 matrix The deflnitions of the determinants of A and B are.
If Eis an elementary matrix for a multiply rule with multiplier m6 0 thendetEA mdetA. Product Notation Induction Logical Sets. DetA a b c d.
A b c d ad bc. Linear algebra - Proving determinant product rule combinatorially - Mathematics Stack Exchange. The determinant of the matrix product equal to the product the determinants of.
The determinant of a permutation matrix P is 1 or 1 depending on whether P exchanges an even or odd number of rows. Cramers 2 2 rule in determinant notation is x f d e b a b c d. This is because of property 2 the exchange rule.
On the one hand ex. Definition The transpose of an m x n matrix A is the n x m matrix AT obtained by interchanging rows and columns of A Definition A square matrix A is symmetric if AT A. Ameans the determinant of matrix A and a bmeans to.
These equations con rm that X B 1A 1 is the unique matrix. IfA2IRmn a matrix andv2IRn1 a vector then the matrix product AvSAv. The notation for absolute value is used to indicate the determinant of eg.
From these three properties we can deduce many others. Any matrix has a unique inverse if its determinant is nonzero. DetA Xn i1 ai1Ai1 and detB Xn i1 bi1Bi1.
The boldface product ad is the product of the main diagonal entries and the other product bcis from the anti-diagonal. The determinant of a 22 2 2 matrix a b c d a b c d is defined to be adbc a d b c. Then the inverse of the matrix product AB exists and is the reverse product B 1A 1 of the inverses.
The determinant of the inverse is the reciprocal of the determinant.

Matrices Adding Multiplying Gaussian Elimination Cramer S Rule 3x3 Matrix Youtube

Sarrus Rule How To Fast Calculate The Determinant Of A 3 X 3 Matrix Linear Algebra Youtube

Cross Product Determinant Method Youtube

Determinant Of A 2x2 Matrix Video Khan Academy

The Determinant Of A 3 X 3 Matrix General Shortcut Method Studypug

7 7 Determinants Cramers Rule Section 7 7
Chapter 16 Matrices And Determinamts

How To Find The Determinant Of A 3x3 Matrix 12 Steps

Product Of Determinants Definition Solved Example Problems

Properties Of Determinants Of Matrices Geeksforgeeks
How To Find The Determinant Of A 4x4 Matrix Youtube

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 38 Of 48 Using The Product Rule And Others Youtube

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 29 Of 48 Product Of Determinants 3x3 Youtube
Multiplication Of Determinants What Is Multiplication Of Determinants Examples Solutions Cuemath

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 30 Of 48 Rule Of Addition 2x2 Determinants Youtube