Identity Matrix Multiplied By Itself
In math symbol speak we have A A sup -1 I. 2 By multiplying any matrix by the unit matrix gives the matrix itself.

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps
This property of leaving things unchanged by multiplication is why I and 1 are each called the multiplicative identity the first for matrix multiplication the latter for numerical multiplication.

Identity matrix multiplied by itself. This means that if you multiply any matrix A by identity matrix I the result is the matrix A it does not matter if identity matrix is on the left or on the right. Multiply A on the left with A T giving B A T A. The reason is that the pivots of B are always at the main diagonal.
I would like this to become more intuitive. My answer is then just the inverse of A because what is multiplied by the identity matrix is itself. On the one side of the equation as A-1b.
If this is new to you we recommend that you check out our matrix multiplication article. The multiplicative inverse of a matrix is the matrix that gives you the identity matrix when multiplied by the original matrix. On the identity matrix R 1 R 2.
An identity matrix is a square matrix whose diagonal entries are all equal to one and whose off-diagonal entries are all equal to zero. The inverse matrix is B 1 A T A 1 A 1 A T. This tells you that.
Like for m x n matrix C we get. Matrix multiplied by itself n times equals identity. A nparray 123 456 B nparray 123 456 print Matrix A isnA print Matrix A isnB C npmultiply AB print Matrix multiplication of matrix A and B isnC The element-wise matrix multiplication of the given arrays is calculated in the following ways.
The number 1 is called the multiplicative identity for real numbers. It can be obtained by multiplying row 2 of the identity matrix by 5. That is any number times 1 is equal to itself.
Multiplying a matrix by the identity matrix I thats the capital letter eye doesnt change anything just like multiplying a number by 1 doesnt change anything. In other words we are performing on the identity matrix 5R 2 R 2. The inverse can of B can be determined by employing our special matrix inversion routine.
Matrix A 2x2 R1 -1 -1 R2 -7 3 Matrix b 2x2 R1 10 R2 0 1 Ab _____ To solve I put. It is shown to be incorrect2x2 R1 -3 -1 R2 -7 -1 Please help. Given a A R 100 100 and A 6 I 100 and A 14 I 100 ist say A 2 I 100 too.
In particular their role in matrix multiplication is similar to the role played by the number 1 in the multiplication of real numbers. As the multiplication is not always defined so the size of the matrix matters when we work on matrix multiplication. Identity matrices play a key role in linear algebra.
The identity property of multiplication states that when 1 is multiplied by any real number the number does not change. There is a matrix which is a multiplicative identity for matricesthe identity matrix. Definition of identity matrix The identity matrix denoted is.
For any whole number n theres a corresponding Identity matrix n x n. Example 98 2 4 1 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 1 3 5 is an identity matrix. The identity matrix is the only matrix for which.
In matrix multiplication each entry in the product matrix is the dot product of a row in the first matrix and a column in the second matrix. Example 97 2 4 1 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 1 3 5 is an elementary matrix. A I I A A.
See the first reference.
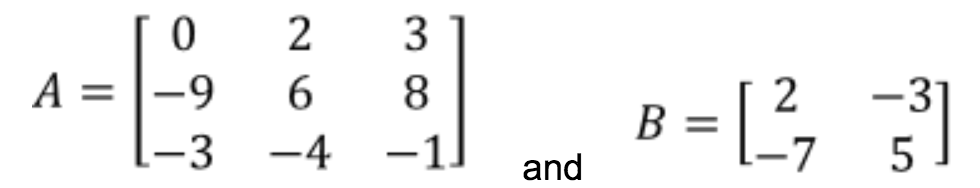
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps

Multiplication Properties Foldable Basic Math Skills Math Instruction Math Multiplication

Pin On Teas Math Prep Study Tips For Teas 6 Math Section

Multiplication Strategy Poster Upper Elementary Math Elementary Math Math Quotes

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps

What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps
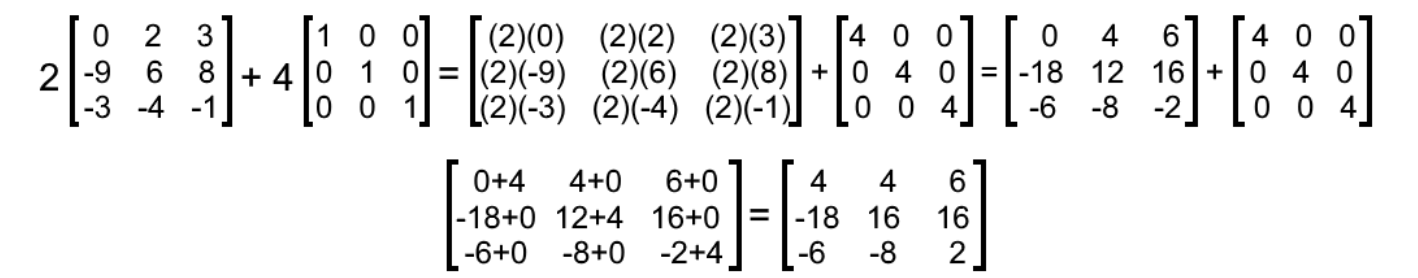
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug
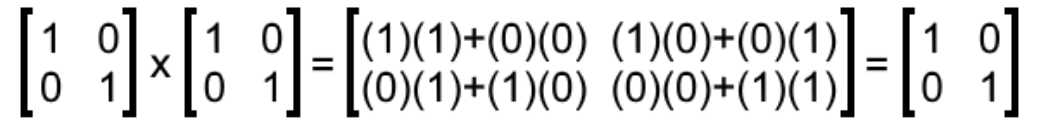
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug
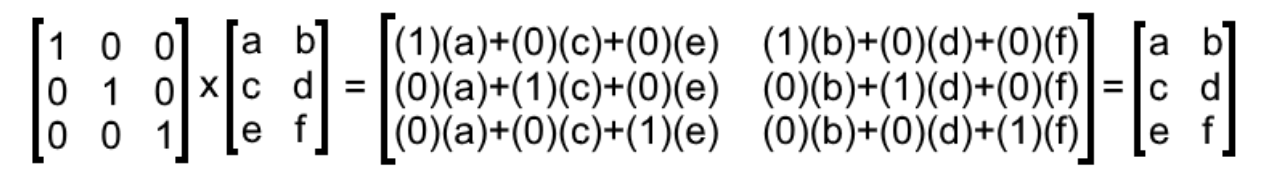
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps

The Identity Matrix And Its Properties Mathbootcamps
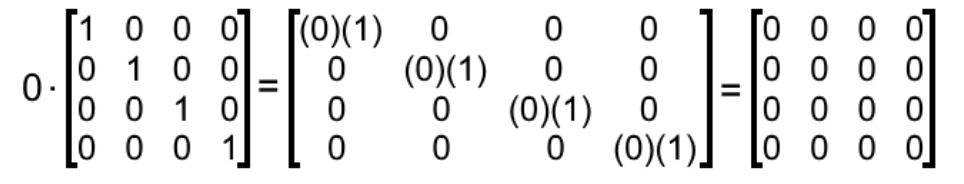
What Is An Identity Matrix Studypug




